For any business, irrespective of its size of operations, small or medium or large scaled enterprises, it is always important to keep track of money that flows into the business. Once an invoice is issued by you, you as a prudent businessman want to ensure that every one of them is paid so that you have a healthy cash flow.
As a businessman, you also want to keep your customer relationship healthy and show a professional and courteous approach to money management. Here, in this scenario, maintenance of documents such as payment receipts and payment advice notes comes in very handy for any business.
What is payment advice or payment advice note?
Payment advice note is a document or letter of communication sent by a customer or buyer to businesses which states that an invoice has been paid to vide cheque, NEFT, RTGS or by any means of electronic transfers etc.,
It is a letter of communication that acknowledges the seller as to which outstanding invoices have been cleared by the buyer and by what means. Therefore, a payment advice note can be very useful when it comes to matching payments to an invoice.
Difference between payment receipt and payment advice note
| Payment receipt | Payment advice notes |
| A payment receipt is a document showing the proof of payment issued by the supplier
It is usually issued by the supplier to the customer to acknowledge receipt of payment. |
Payment advice is sent by customers to the seller
This is issued by the customer to the supplier that an invoice has been paid and it provides the invoice reference and date as well. |
Components of payment advice
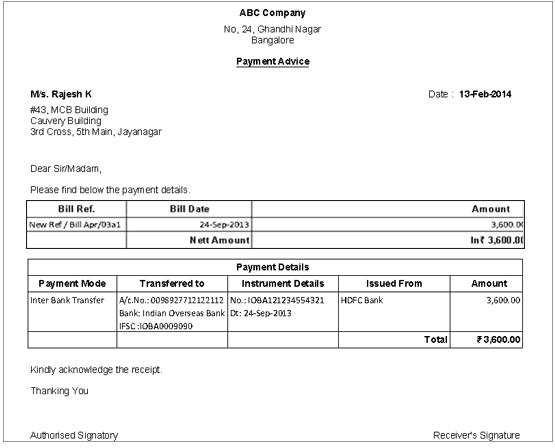
Payment advice should contain the following information :
- The date on which payment advice was drafted.
- A reference to invoice number or invoice number against which the payment has been made.
- The amount of payment against such invoice
- The method of payment such as Cheque, NEFT, RTGS etc.,
Sample payment advice format
How do businesses generate payment advice?
Today, most businesses are using accounting software to manage the books which comes with the inbuilt capability to generate various statements including payment advice. Also, managing the outstanding bills portfolio has become very simple with the help of ERP software. It allows you to know the bills which has been paid and which has been outstanding due.
Payment advice processed using accounting software helps to ensure the professional standards have been followed as receipts can be easily tracked against the invoices in real-time.
Using Tally.ERP 9, makes it easier to generate payment advice and send it to suppliers/other parties along with the cheques/other instruments. It is fully flexible to add or remove the additional details from payment advice to meet your business needs.